Tel: +86-17507082182
Email: sales@juvotron.com
WhatsAPP: +86-17507082182

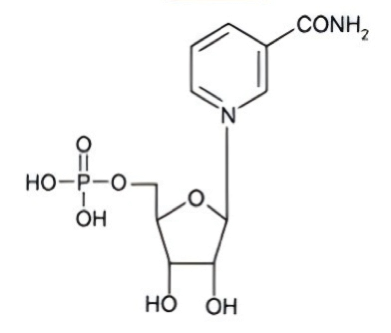

| Cas No. | 1094-61-7 |
| Molecular Formula | C11H15N2O8P |
| Purity. | ≥98% |
| Molecular Weight | 334.21g/mol |
| Chemical Name | β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide |
| Synonyms |
NMN |
| CAS No. | 1094-61-7 |
| Molecular Formula | C11H15N2O8P |
| Molecular Weight | 334.21g/mol |
| Appearance | |
| Storage and Shipping Conditions | |
| Industries | Cosmetic raw materials, functional dietary supplements |
| Applications | |
| Description | β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (commonly abbreviated as NMN) is a naturally occurring compound that plays a crucial role in the production of NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), a vital coenzyme in cellular metabolism. NMN is a precursor to NAD+, meaning it is one of the building blocks the body uses to generate NAD+, which is involved in critical processes like energy production, DNA repair, and maintaining cellular health. |